How does an Induction Motor work
The AC induction motor is well
suited to applications requiring constant speed operation. In general, the
induction motor is cheaper and easier to maintain compared to other
alternatives.
The induction motor is made up of
the stator, stationary windings, and rotor. The stator consists of a
series of wire windings of very low resistance permanently attached to the
motor frame. As a voltage and a current are applied to the stator winding
terminals, a magnetic field is developed in the windings. By the way, the stator
windings are arranged, and the magnetic field appears to synchronously rotate
electrically around the inside of the motor housing.
The rotor is comprised of a number of thin bars,
usually aluminum, mounted in a laminated cylinder. The bars are arranged
horizontally and almost parallel to the rotor shaft. At the ends of the rotor,
the bars are connected together with a “shorting ring.” The rotor and stator
are separated by an air gap which allows free rotation of the rotor.
Induction Motor:
The induction motor is very much important for the industrial revolution. Every electrical engineer and electrical crew related to the work field of Induction motors should have a clear conception.
This video clip of "How does Induction Motor work" will be quick and helpful.
Single-phase induction motors are used extensively for smaller loads, such as household appliances like fans. Although traditionally used in fixed-speed service, induction motors are increasingly being used with variable-frequency drives (VFDs) in variable-speed service.
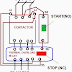
A three-phase Induction Motor is Self Starting. When the supply is connected to the stator of a three-phase induction motor, a rotating magnetic field is produced, the rotor starts rotating and the induction motor starts. At the time of starting, the motor slip is unity, and the starting current is very large.
As the motor accelerates the slip reduces and the voltage induced in the rotor also get reduced. To limit this starting current the starter is used to start the induction motor. Reducing the stator voltage- Star-delta starter. Adding external resistance to the rotor circuit- For slip ring motor.
A three-phase Induction Motor is Self Starting. When the supply is connected to the stator of a three-phase induction motor, a rotating magnetic field is produced, the rotor starts rotating and the induction motor starts. At the time of starting, the motor slip is unity, and the starting current is very large.
As the motor accelerates the slip reduces and the voltage induced in the rotor also get reduced. To limit this starting current the starter is used to start the induction motor. Reducing the stator voltage- Star-delta starter. Adding external resistance to the rotor circuit- For slip ring motor.




No comments:
Post a Comment
WAZIPOINT:
Thank you very much to visit and valuable comments on this blog post. Keep in touch for next and new article. Share your friends and well-wisher, share your idea to worldwide.